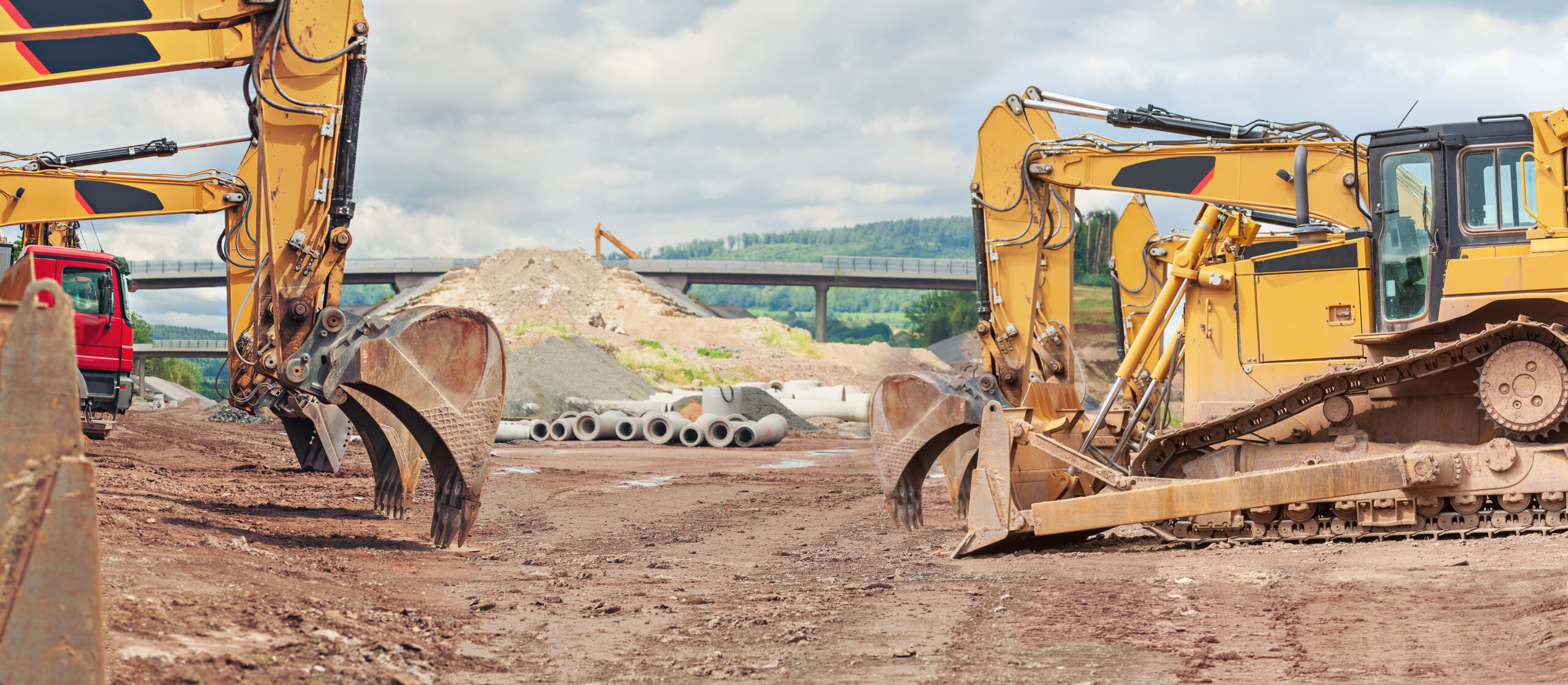
Technical Name: NR 12 TRAINING COURSE – MACHINERY AND EQUIPMENT
Reference: 34783
We offer courses and training in technical language: Portuguese, English (Regional), Croatian, Japanese, Spanish, French, Chinese (Regional), German, India (Regional), Arabic, Korean, Russian, among others.
What is the objective of the NR 12 – Machinery Safety Course?
The objective of the NR 12 course is to train professionals to operate, maintain, and inspect machines and equipment safely, in accordance with the legal requirements established by the standard. Therefore, it aims to ensure the physical integrity of the worker and prevent accidents through the understanding of mechanical, electrical, and organizational risks associated with the equipment.
More than a legal requirement, the NR 12 – Machinery Safety Course awakens in the operator a broader awareness of their role. Each machine carries an energy field, and operating it with full attention means acting in harmony with that vibration, making safety a natural extension of presence.
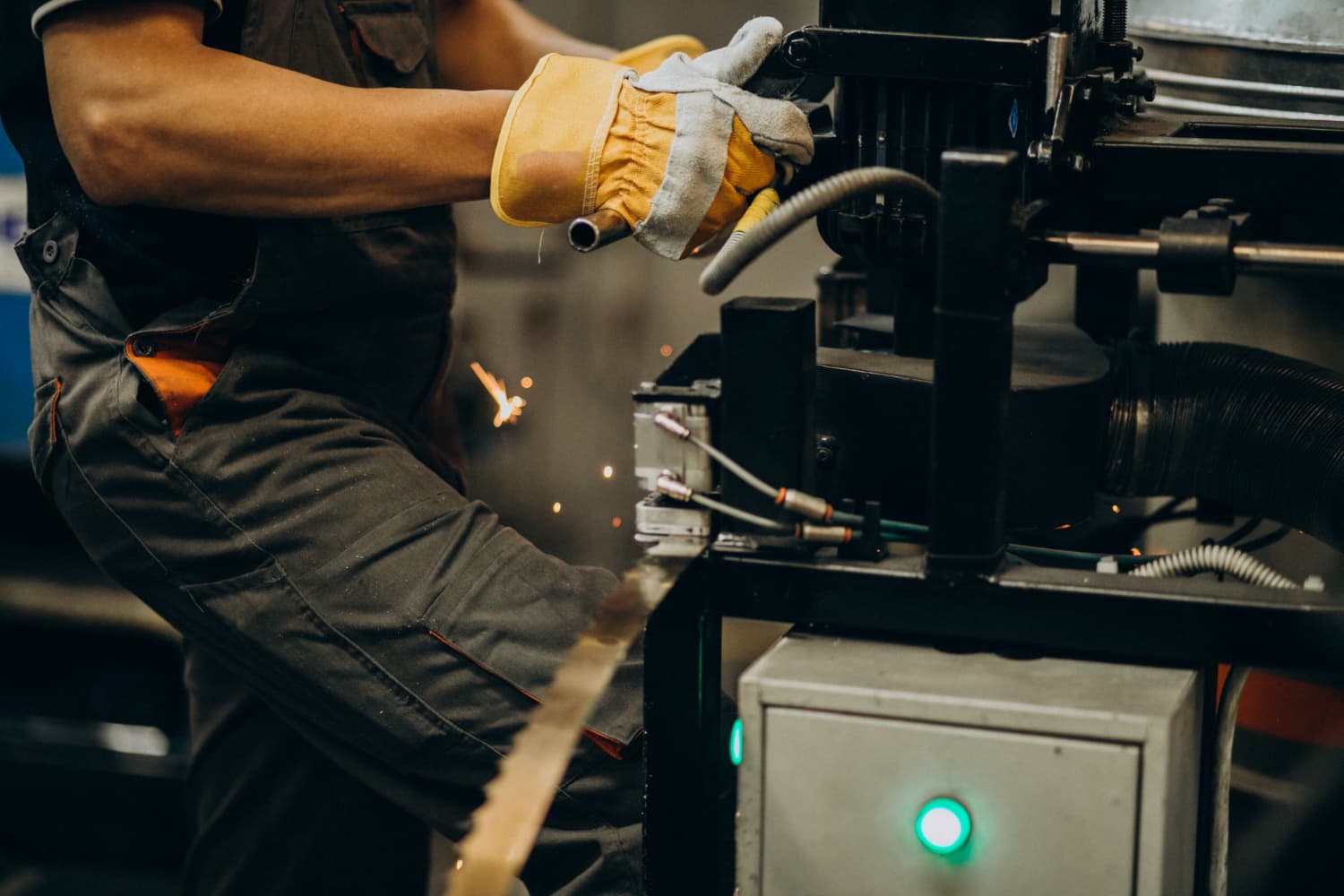

Saw operation requires appropriate PPE, fixed guarding, and emergency stop devices in accordance with NR 12. Safety arises from technical precision and conscious presence.
What types of protections are provided for under NR 12?
NR 12 categorizes protections to isolate or prevent access to hazardous parts of machines. The main types include:
| Protection Type | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|
| Fixed Guards | Non-removable barriers that prevent direct contact |
| Movable Guards | Can be opened/moved, require interlocking devices |
| Safety Devices | Sensors, light curtains, emergency stop buttons |
| Complementary Protections | Audible/visual alarms, signs, enclosures |
How should periodic inspections of machine safety protections be carried out?
Inspections must be systematically scheduled, conducted by a qualified professional, and formally documented. The process must verify:
Physical integrity of guards;
Proper functioning of sensors and interlocks;
Correct mounting, no gaps or damage;
Signs of tampering or bypass attempts.
Inspection records should be kept in spreadsheets or management software, with supporting reports and photos. When done with full awareness, inspection becomes more than a routine—it becomes an act of energetic and collective protection.
What are the most common risks associated with the lack of mechanical protection in industrial equipment?
The absence of proper mechanical guarding increases the following risks:
Crushing: Between moving and fixed parts (NR 12.4.1);
Amputation: At shear or cutting points (NR 12.4.6);
Entanglement: By exposed belts, pulleys, chains, or shafts;
Flying particles: In cutting or machining processes without enclosure;
Accidental contact: With heated surfaces or energized components.
These risks are mitigated through physical barriers, enclosures, emergency stop systems, and ongoing operator training. Ignoring such measures is equivalent to allowing chance to govern safety.
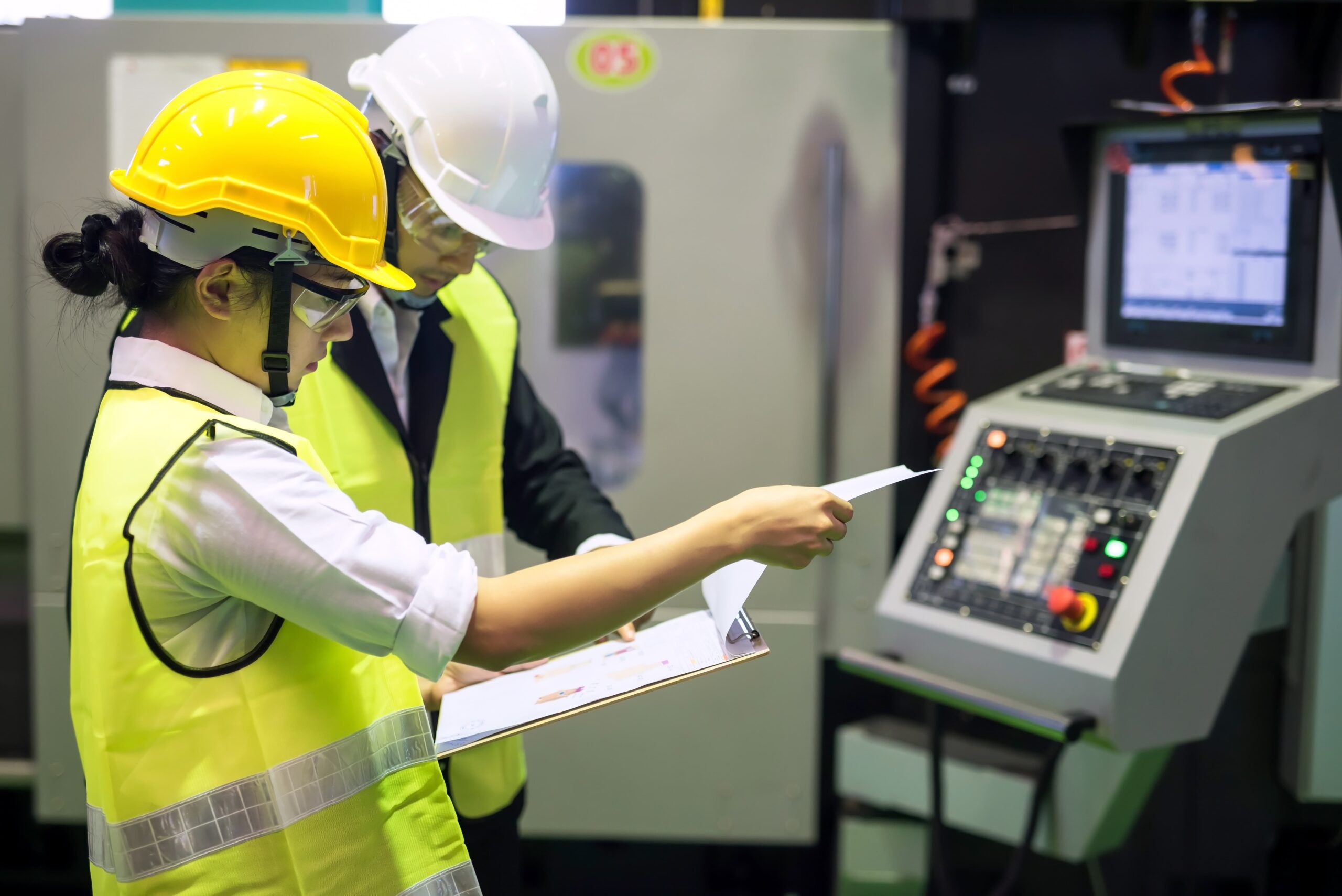

Technical inspection of CNC machines must validate interlocks and operational safety. Compliance with NR 12 and ISO 13849-1 ensures safe operation.
Does NR 12 allow the use of old machines that do not meet current safety requirements?
According to NR 12 (item 12.1.4), all machines and equipment in operation must comply with the standard, regardless of their manufacturing date. Older machines must therefore be retrofitted or upgraded with safety devices, based on risk assessments.
Furthermore, employers must ensure that operators are trained to identify residual risks (item 12.15). Noncompliance can be classified as a serious and imminent risk, subject to immediate shutdown by labor inspectors.
What are the main penalties for companies that do not comply with NR 12?
Noncompliance with NR 12 exposes companies to administrative, civil, labor, and even criminal consequences:
| Penalty | Legal Basis | Direct Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Administrative Fines | NR 28 – Annex II | Immediate financial loss |
| Embargo / Interdiction | NR 3 | Operational shutdown |
| Labor lawsuits | CLT + case law | Compensation, pensions, reinstatement |
| INSS Regressive Lawsuits | Law 8.213/91, art. 120 | Reimbursement of social security expenses |
| Reputational and certification losses | Market, ISO standards | Loss of contracts and credibility |
What are the key elements to ensure safety devices are not only installed but properly aligned with their intended function?
To ensure the effectiveness of safety devices, the following five pillars must be met:
Design Based on Risk Assessment (ISO 12100, ISO TR 14121-2):
Identification of mechanical, electrical, thermal, ergonomic hazards;
Risk classification and determination of required Performance Level (PLr).
Installation with Functional Validation (Commissioning):
Inspection prior to operation;
Fail-safe and redundancy testing.
Performance Level (PL) according to ISO 13849-1:
PLr calculated based on exposure frequency, possibility of avoidance, and potential harm;
System implementation from category 2 to 4 depending on criticality.
Preventive Maintenance and Testing:
Scheduled intervals;
Documented evidence;
Technical manager designated with ART (Technical Responsibility Annotation).
Training and Operational Awareness:
Operators must understand the purpose of the protection, how to act in failures, and how to report deviations.
A protection device only fulfills its function when the operator is present, focused, and oriented toward prevention.
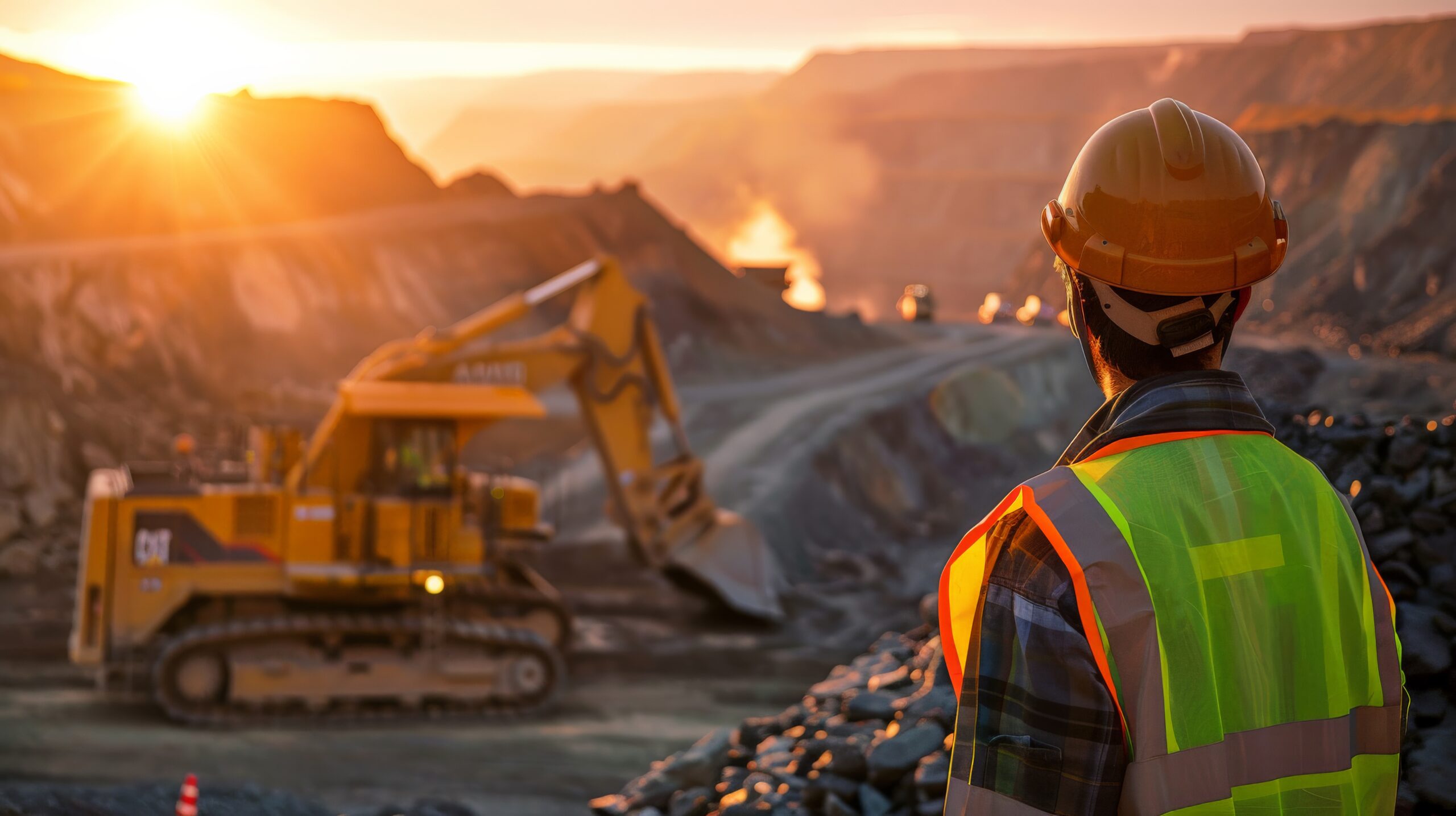

Excavator supervision in a mining area. Application of NR 12 and NR 22 standards, use of PPE, and risk analysis ensure safety and operational control with conscious presence.
Why is the NR 12 – Machinery Safety Course mandatory in industrial environments?
The obligation is defined in item 12.15.1 of NR 12, which states that workers authorized to operate, maintain, inspect, or intervene in machines must receive specific training compatible with their duties. This includes:
Safety principles;
Types of risks;
Protection systems;
Emergency and lockout/tagout procedures (LOTO)
Safe operation under normal and abnormal conditions.
NR 1 (General Provisions) also reinforces that training is a prerequisite for authorizing work involving occupational risk.
Do you still believe that operating a machine without specific training does not pose serious risks to physical integrity?
That belief directly contradicts statistical data and legal precedents. Over 70% of industrial amputations occur with untrained workers or those unaware of safe operational procedures.
Brazilian labor courts recognize that failure to train constitutes employer negligence, worsening indemnification penalties. Even when the worker acknowledges misconduct, the company remains liable for culpa in vigilando (failure to supervise) and culpa in eligendo (failure to select properly).
See Also:
Laudo de Esmerilhadeira NR 12
Curso Operação Sala de Máquinas
Laudo Máquinas de Moldagem por Sopro
Certificado de conclusão
NR-12 Machines Course in English
NR 12 TRAINING COURSE – MACHINERY AND EQUIPMENT
Total Duration: 16 Hours
Module 1 – (2 hours):
Description and identification of the risks associated with each machine and equipment, and the specific protections against each of them.
Module 2 – (2 hours):
Operation of safety devices; how and why they should be used.
Module 3 – (2 hours):
How and under what circumstances a safety device can be removed, and by whom—typically only by inspection or maintenance personnel.
Module 4 – (2 hours):
What actions to take—for example, contacting the supervisor—if a safety device is damaged or has lost its function, no longer ensuring proper safety.
Module 5 – (2 hours):
Safety principles in the use of machinery or equipment.
Module 6 – (2 hours):
Safety measures for mechanical, electrical, and other relevant hazards.
Module 7 – (2 hours):
Safe working method.
Module 8 – (2 hours):
Work permits and lockout/tagout system during inspection, cleaning, lubrication, and maintenance operations.
Course Completion and Certification:
Practical Exercises
Evidence Records
Theoretical Assessment
Practical Assessment (When contracted)
Certificate of Participation
Observation:
The program content presented follows the guidelines established by Regulatory Standard NR 12, which addresses occupational safety when working with machinery and equipment. All instructions covered are in compliance with legal requirements, ensuring worker protection and equipment integrity, with the goal of preventing accidents and promoting a safe and healthy work environment.
Note:
We emphasize that the General Normative Training Syllabus may be modified, updated, or have items added or removed as deemed necessary by our Multidisciplinary Team.
Our Multidisciplinary Team is authorized to update, adapt, modify, and/or exclude content, including the inclusion or exclusion of Standards, Laws, Decrees, or technical parameters they deem applicable—whether directly related or not. The contracting party is responsible for ensuring compliance with applicable legislation.
NR-12 Machines Course in English